According to new guidelines from an expert panel sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease (NIAID), babies should be introduced to peanuts in a controlled way as early as 4 to 6 months of age. These new guidelines, published on January 5th, are largely based on findings from the 2015 LEAP study. NIAID’s expert panel included representatives from 25 professional organizations, federal agencies, and patient advocacy groups.
Introducing peanut early to high-risk infants diets can dramatically reduce the risk for allergic sensitization. The LEAP study showed early introduction of peanut protein to be associated with an 81% reduction in peanut allergy among high-risk children. Infants with severe eczema, an egg allergy, or both are considered to have a “high risk” for peanut and other food allergies.
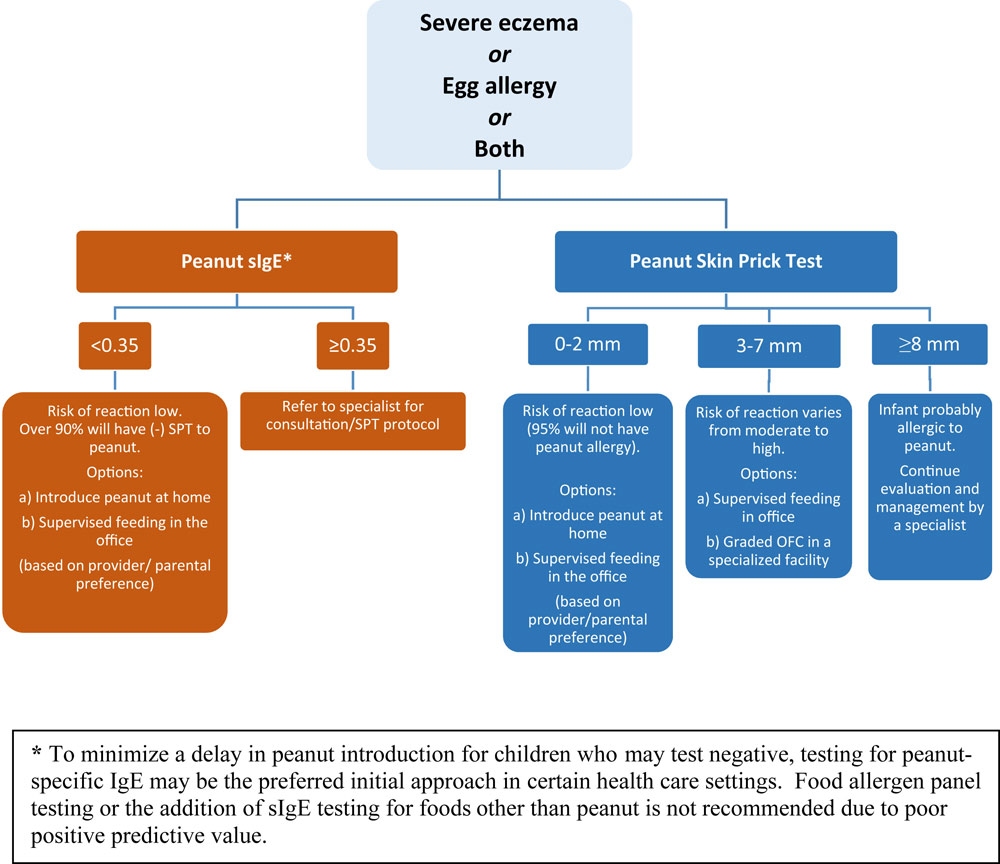
The revised guidelines, published on January 5th, recommend that peanut-containing foods should be given to high risk babies as early as 4-6 months, after evaluation by the baby’s healthcare provider or a specialist. The expert panel recommended that evaluation with peanut-specific IgE measurement, skin prick testing, or both be “strongly considered before the introduction of peanut to determine if peanut should be introduced and, if so, the preferred method of introduction.”
The expert panel included separate guidelines for infants with different peanut allergy risks. The figure below provides the recommended approaches for evaluation of children with severe eczema, egg allergy, or both before peanut introduction.
Addendum guidelines for the prevention of peanut allergy in the United States: Report of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease





COMMENTS